The definition of fast charging
What is fast charging, is it judged by power? Is it judged by voltage? Is it judged by the interface? This has to be considered comprehensively. For the definition of fast charging, there is currently no relevant organization that has made a clear judgment. Everyone has their own understanding of fast charging.
Fast, different from slow, can only be judged by reference.
The USB standard power supply voltage is 5V, and the iPhone 11 uses Apple’s 5V1A 5W charging, which is definitely included in the slow charging. Instead, use the APPLE2.4A protocol to achieve 12W charging power, or use USB-C to Lightning to obtain more than 18W power through the PD charger, both of which are fast charging. In the Android camp, those that increase the voltage through QC can also be included in fast charging, VOOC, SCP, etc. that change low voltage and high current are also fast charging, and PD super-high-power charging is of course also fast charging.
To put it simply, the methods of increasing the charging power can be summarized as fast charging.
When did the fast charge come out?

As early as the Nokia era, most electronic products used battery replacement as a means of maintaining battery life. Electronic products at that time had a single function and low power consumption, so there was no demand for fast charging in the market.

Until the launch of the Samsung Note Series of big-screen mobile phones, the output voltage of the matching charger is not 5V but 5.3V, and it has a loss compensation function to offset the voltage drop loss of the wire to increase the charging power. At this time, users find that the charging speed of this charger is faster than other 5V chargers, so the experience of “fast charging” was vaguely born for the first time.

In 2014, OPPO launched the Find7 mobile phone equipped with VOOC flash charging. It can be charged for five minutes and talk for two hours, but only OPPO users can enjoy this kind of fun. In 2015, a large number of Qualcomm QC2.0 mobile phones were launched. Based on the general technical standards and the selection of various third-party accessories, fast charging officially kicked off at this time, and most users enjoyed the fun of fast charging for the first time.
The unification of USB-C promotes the development of PD fast charging
As early as December 2013, the US USB-IF Association announced the USB-C interface, and then in 2014, the related industry chain was ready for mass production. The USB-C interface supports double-sided blind insertion, which solves the experience of reinserting the front and back of the device with naked eyes. The pins up to 24pin allow the interface to support 100W power transmission and 20Gbps data transmission, and a PPS voltage subset was added to the later PD3.0 standard, which has sustainable development potential.

In 2015, many products equipped with USB-C for the first time were born, the first USB-C mobile phone LeTV super phone 1, the first USB-C notebook New Macbook, the first tablet Nokia N1, the first USB-C charger Apple 29W, the first The new USB-C charging Baoyu Bo YB-CP1, these pioneers have played a role in promoting the rapid popularization of USB PD in the future.
The unification of the USB-C interface makes the industry full of vitality. All kinds of PD fast charging accessories are of high quality and low price. After several years of market development, USB PD fast charging has entered almost all mainstream electronic products in 2020.
The composition of the fast charging system
The fast charging system consists of three major parts, the charger (power adapter) responsible for providing power, the cable (data cable) for power transmission, and the receiving end device (digital product), each of which is a part of the fast charging system By.
1.Fast charging chargers
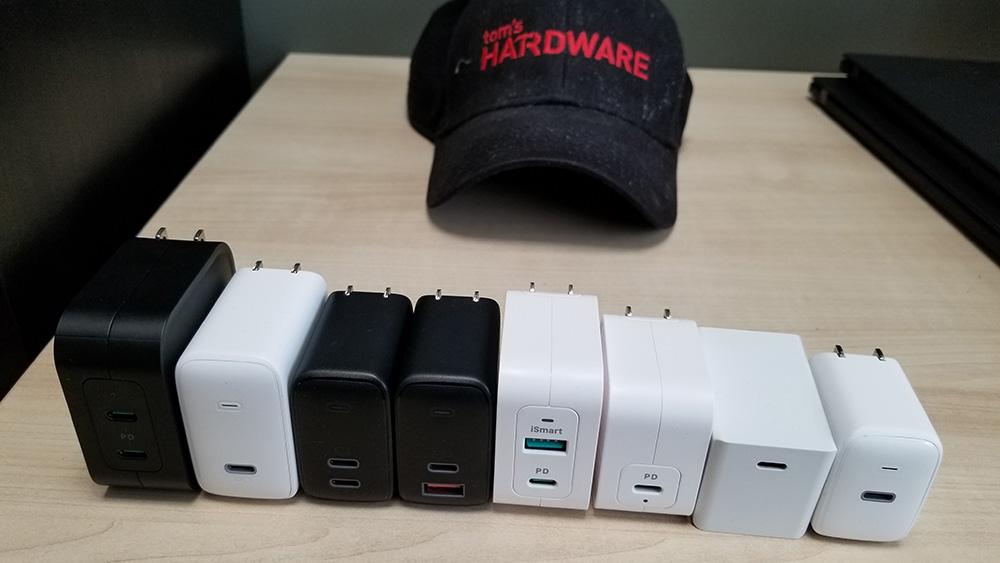

In the past, because of different voltage requirements and different interfaces, each device required a corresponding charger, and the power strips were densely plugged with different chargers. Nowadays, the advanced communication mechanism of USB PD allows different devices to communicate with the charger and ask for the voltage that matches their needs. Whether it is a high-power notebook with up to 100W or a TWS earphone with only a few watts, you can use the same PD charger to charge, and the multi-port charger can also provide one-to-many services.
From the device point of view, the traditional silicon-based charger is huge and inconvenient to carry. To reduce the size of the charger, the switching frequency must be increased. However, the traditional silicon-based semiconductor cannot meet the high-frequency characteristics, so the size of the charger has been maintained at a relatively large level.
In 2018, ANKER successfully mass-produced the first gallium nitride charger, announcing that the charger has entered another dimension. High-frequency and high-efficiency gallium nitride chargers can use smaller transformers, capacitors, inductors and other devices, combined with a three-dimensional stacking design, the volume of gallium nitride chargers is nearly half that of traditional chargers under the same power.
2.Fast charging cables
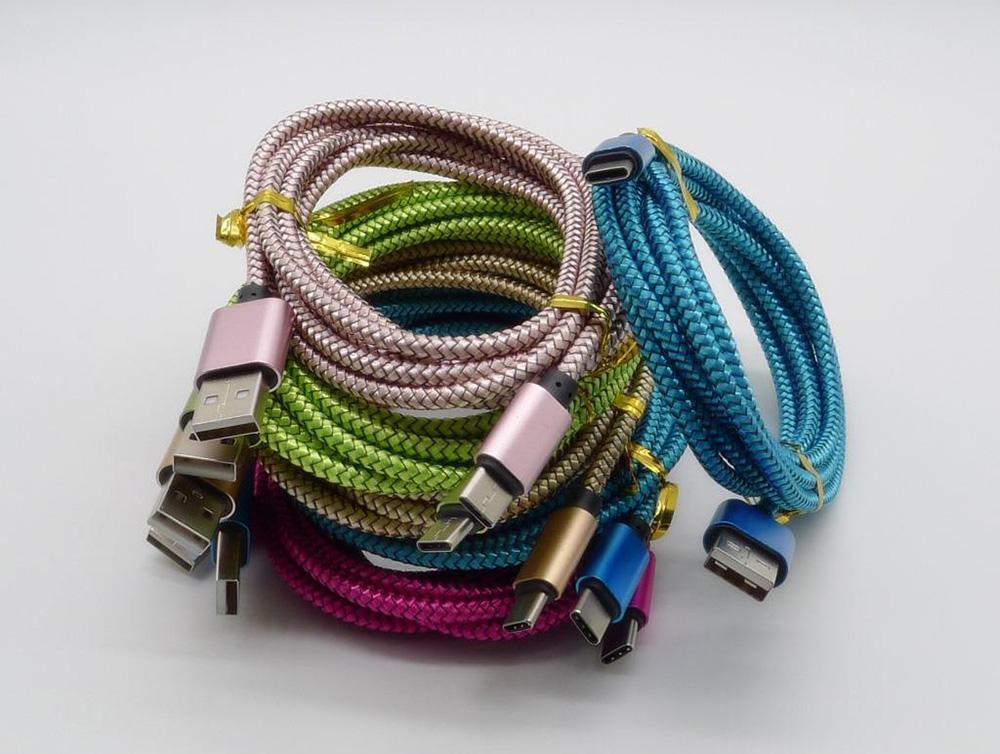

In addition to the charger, fast charging also requires data cables. The data cables used for fast charging are mainly divided into three types: USB-C to USB-C, USB-C to Lightning, and USB-C to USB-A.
USB-C to USB-C is also known as the CC cable. According to the cable specification and whether it has a 5A E-Marker chip, it can be divided into 60W power transmission cable and 100W power transmission cable. If users need more than 3A current, they must use 5A E-Marker cable. CC cable has become the most common cable for Android phones, tablets, and notebooks.
USB-C to Lightning is a special cable launched by Apple for connecting to PD chargers. Applicable devices include Apple devices such as iPhone, AirPods, and mid-to-low-end iPads. As a Lightning cable, each cable needs to pass MFi certification.
There are two types of USB-C to USB-A, one is special specifications mainly used for some special fast charging devices, such as Huawei low-voltage fast charging SCP, OPPO low-voltage fast charging VOOC, Xiaomi’s private magic change fast charging; The other is a general-purpose cable, which does not support PD fast charging, but only supports QC, AFC, FCP, PE and other fast charging.
3.Fast charging devices
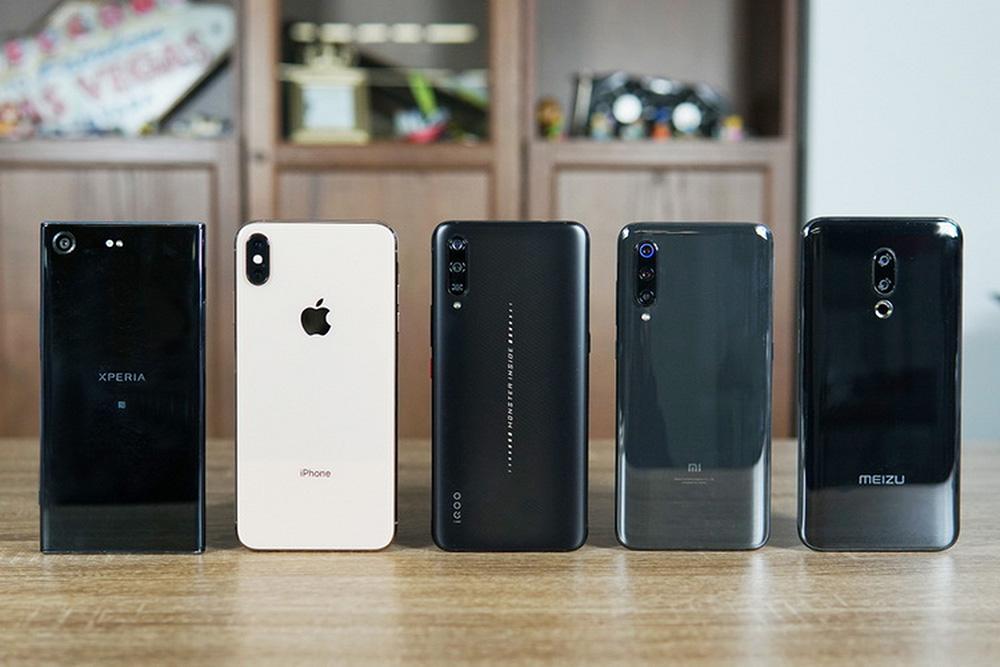

In 2020, most digital products support fast charging, and mainstream devices such as Android phones, iPhone 8 and later models, iPads, notebooks, game consoles, TWS earphones, and smart wearables all support USB PD charging.
The core of future fast charging technology
Let’s take mobile phones with rapid charging technology as an example. A few years ago, the QC fast charging power of mainstream mobile phones stagnated at 18W for a long time, and the full charging time was about 2 hours. As for why it has been maintained for many years? That’s because it’s okay to use, but the heat brought by the low-cost, simple and rude QC high-voltage fast charge is not a good experience. Therefore, Huawei and OPPO began to take the low-voltage direct charging route, which is faster and does not cause too much heat. Compared with QC, it has a great advantage. The charging speed is about 1 hour, which has been improved to a certain extent.
The following technologies applied to fast charging have been stable and mature. Compared with the slow evolution in the past, they have reached the level of intergenerational upgrades, and can be designated as fast mainstream technologies in the next few years or even ten years.
1.Charge pump

The major step-level leap in fast charging technology happened in 2017. Meizu launched the 55W Super mCharge fast charging technology globally at MWC 2017, demonstrating the very advanced charge pump technology at that time and providing technology for various fast charging development routes in the future. The charge pump chip can provide a voltage dividing function. The charger increases the voltage for transmission without the need for thick wires to transmit large currents, reducing line losses. After entering the mobile phone, it is converted into low voltage and high current through the charge pump.
2.Series direct charging technology
In 2018, OPPO launched the 10V5A high-voltage direct charging technology for batteries in series. The conversion circuit that causes heat in the mobile phone is migrated to the charger, and two 4.4V batteries are connected in series to become an 8.8V battery pack. There is no large voltage difference between the charging voltage and the battery pack voltage, achieving both low heat and fast charging.
3.Graphene batteries
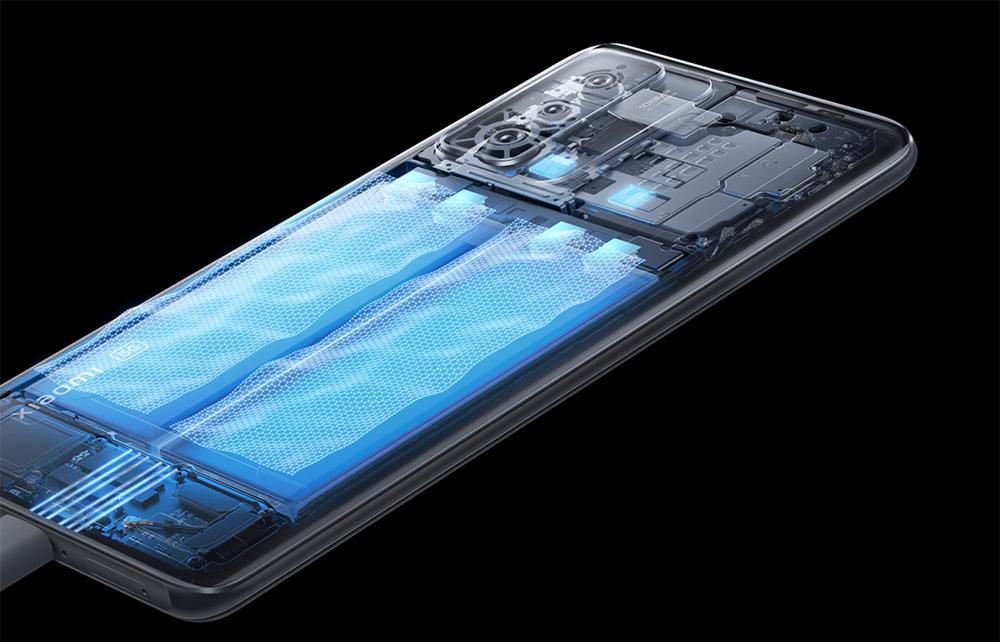

In 2020, the core battery of fast charging finally ushered in a material change. The large-scale mass production of graphene batteries allows ultra-high-power fast charging to break away from PPT drawings. With charge pump and series charging technology, the charging power of mobile phones exceeds 100W for the first time in history. OPPO, VIVO, and Xiaomi have all successfully mass-produced flagship mobile phones with fast charging exceeding 100W, and the charging speed is calculated in minutes.

